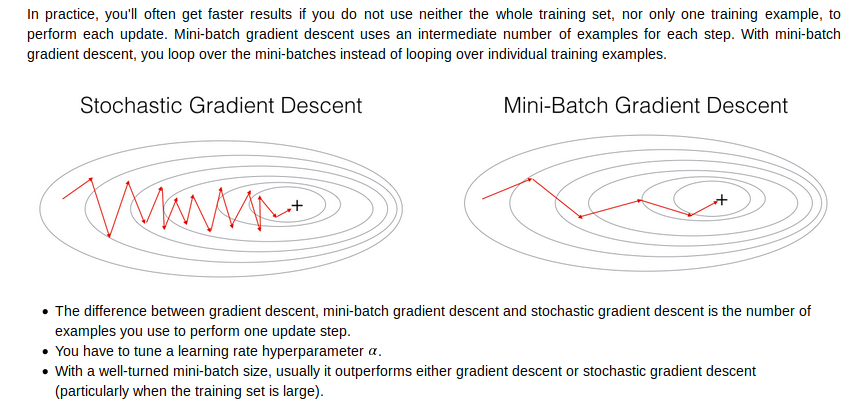
mini batch gradient descent
mini-batch size
- if mini-batch size = m (m=sample size)
(X^[i],Y^[i]) = (X,Y)
收敛速度会很快(步长很大)
end up with batch gradient descent,which has to process the whole training set before making progress
- mini-batch size = 1 又叫做stocastic gradient descent
收敛步长会很小,很有可能会不收敛,而且vectorization会很慢
lose the benefits of vectorization
如下图
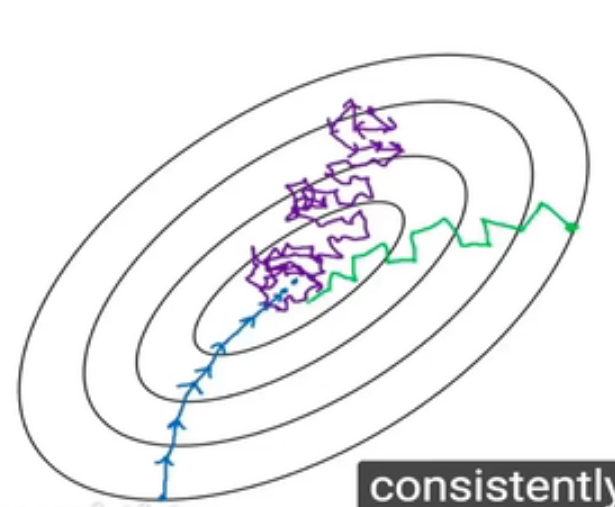
紫色表示batch size=1的收敛,而蓝色表示batch size=m的收敛。
how to choose mini-batch size?
1.通常用 64,128,256,512大小(power of two)


learning rate decay
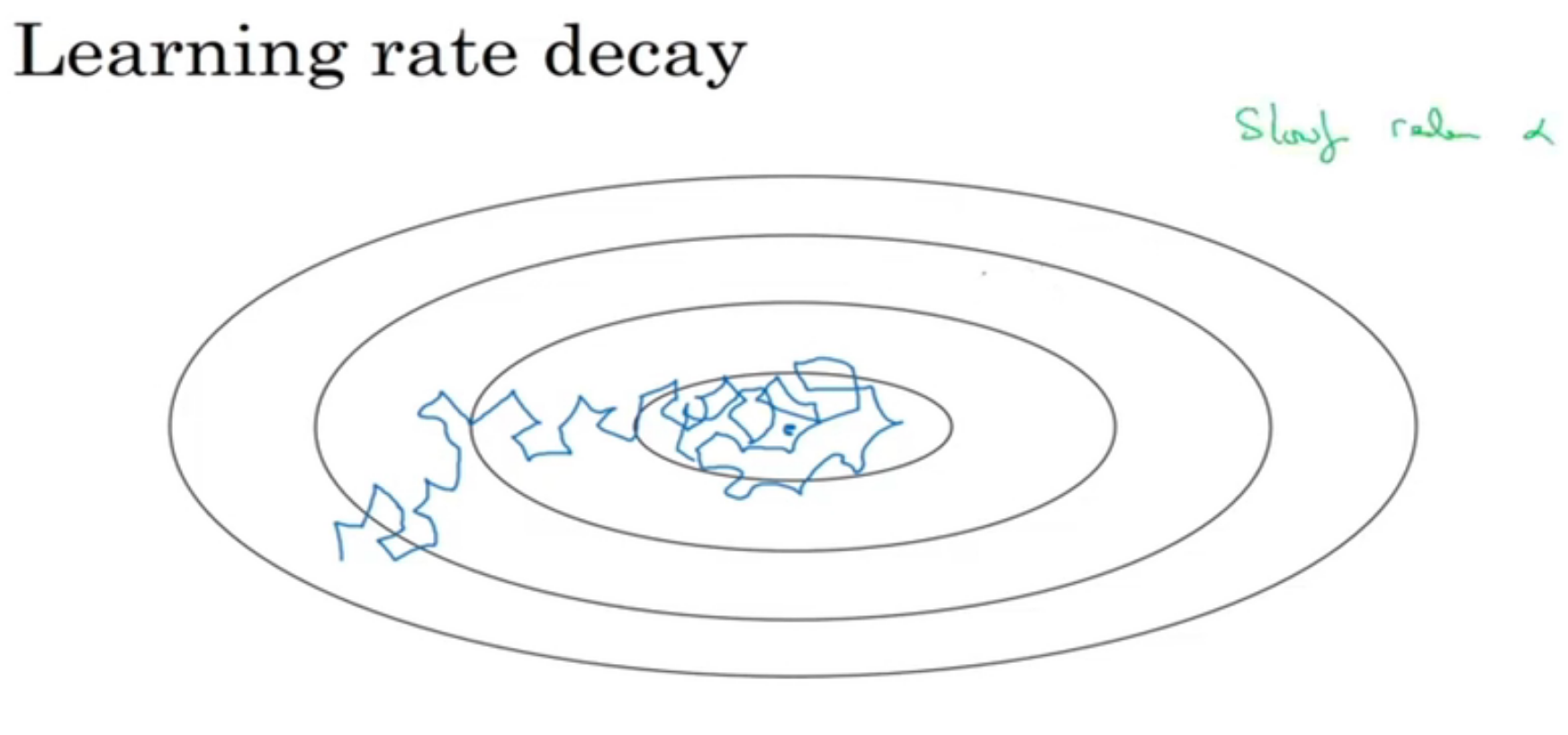
当梯度下降的时候,由于学习率是固定的,因此可能会在最低点附近徘徊而最终不能收敛。
implementation
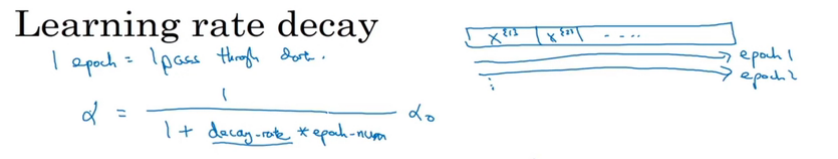
alpha = 1/(1+decay_rate x epoch_num) *alpha
其他方法也可:

mini-Batch gradient descent
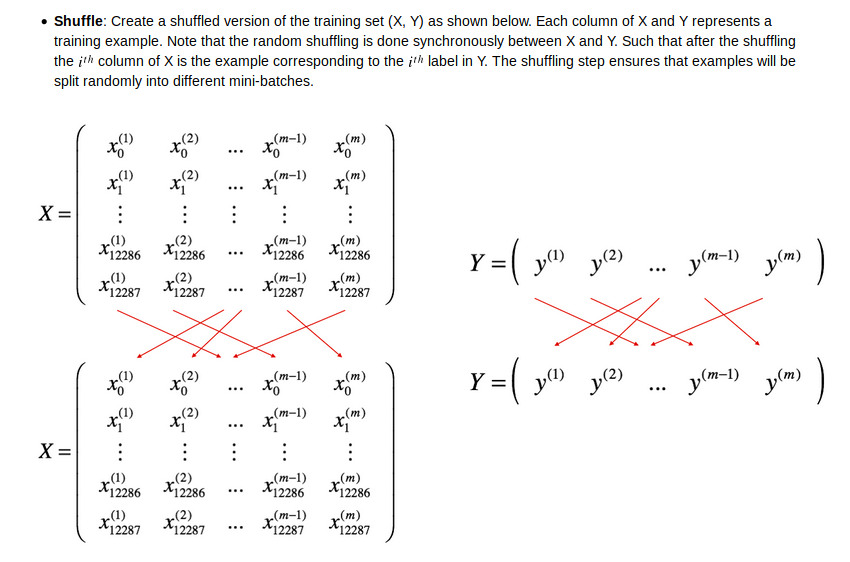
shuffle
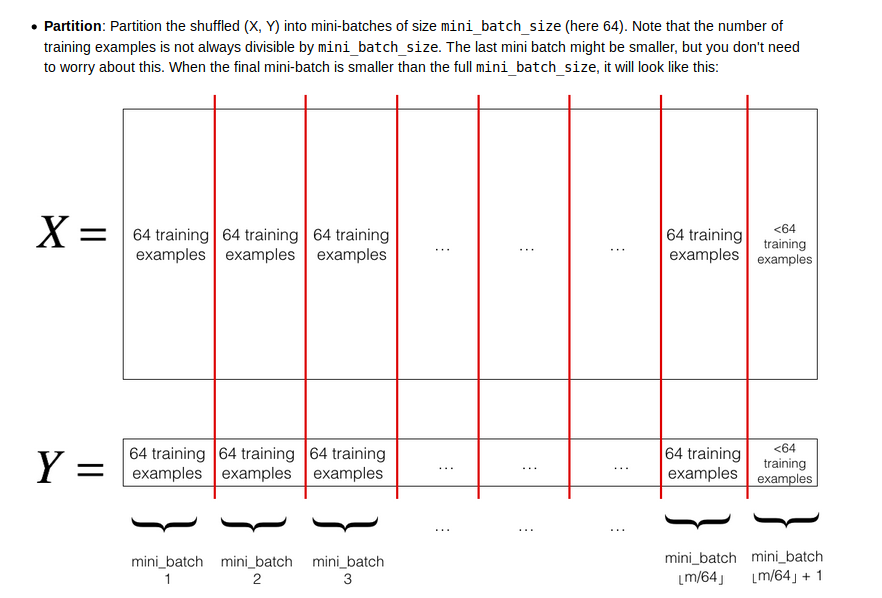
parition
code
注意最后一个batch_size有可能和前面的size不同,因为样本总数可能不等于batch_size的倍数
1 |
|
momentum
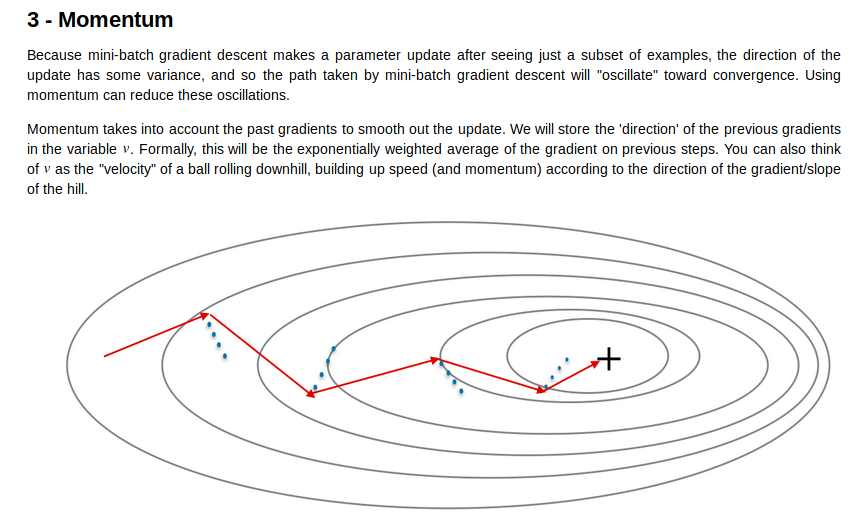
蓝色是gradient的方向,而红色是实际velocity的方向,我们让gradient影响velocty下降的方向
code
1 |
|
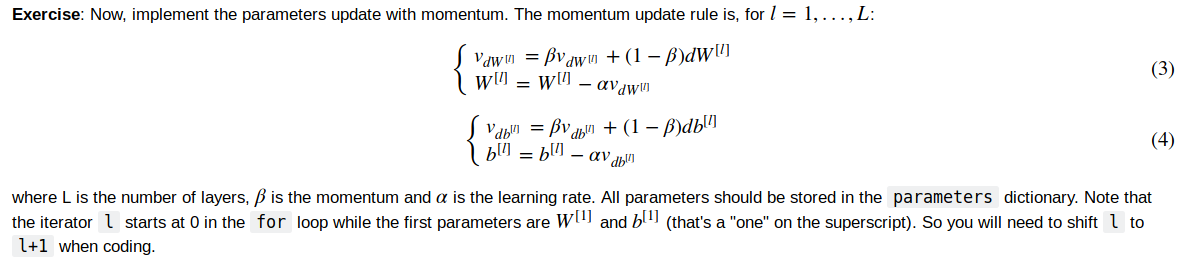
update parameters

Adam optimization

1 | def initialize_adam(parameters) : |
update parameters
1 | def update_parameters_with_adam(parameters, grads, v, s, t, learning_rate=0.01, |
usage
注意每次epoch的时候,分为多个batch学习参数
1 | def model(X, Y, layers_dims, optimizer, learning_rate=0.0007, mini_batch_size=64, beta=0.9, |