参数的初始化
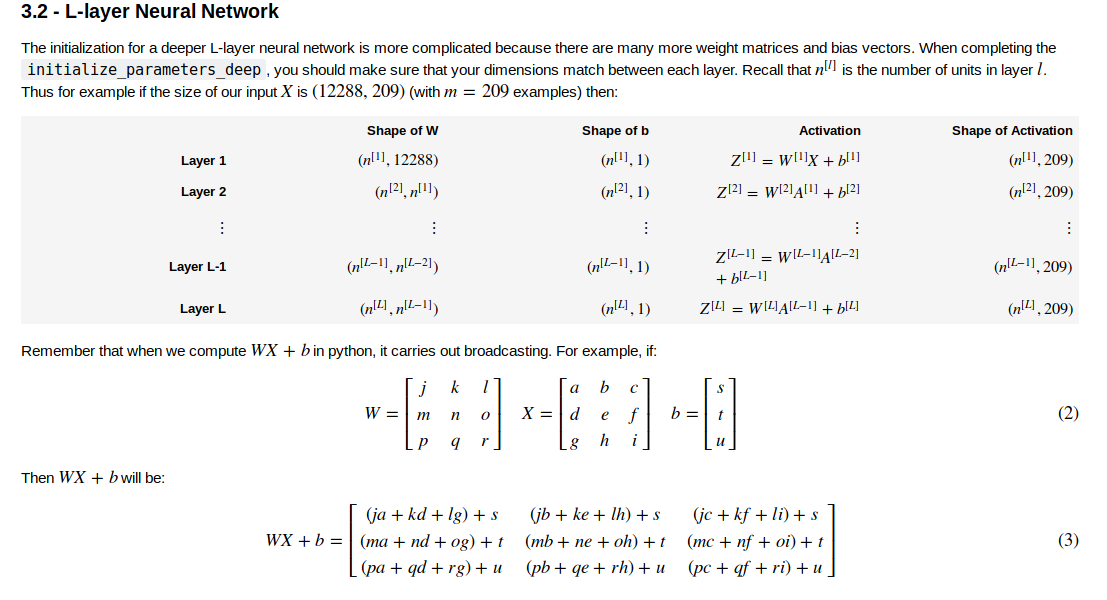
搭建深层的神经网络,各层W,X,B的维度一定要搞清楚
如上图所示,第i层W的维度为(n^[i],n^[i-1])
其中12288是特征数量,209是样本数,n^[i]是第i层神经元的数量。
1 |
|
Forward Propagation

实现Relu或者sigmoid激活函数
1 | def sigmoid(Z): |
以下是linear_activation_forward的函数
1 |
|
对于L层网络的forwarding
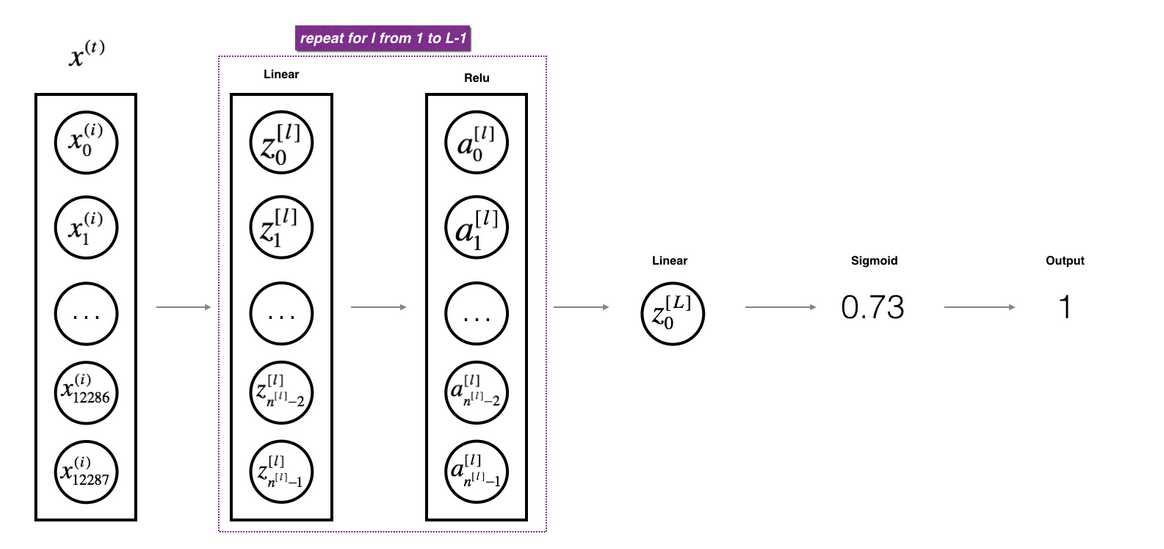
前L-1层作Relu变换,最后一层做sigmoid变换(由于是二分类)
1 |
|
在这里你得到的AL就是经过L曾训练后的parameters,可以用来测试结果,同时所有中间结果都保存在了caches中。
cost function
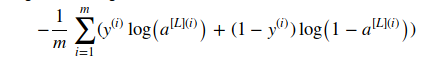
1 |
|
backward propagation
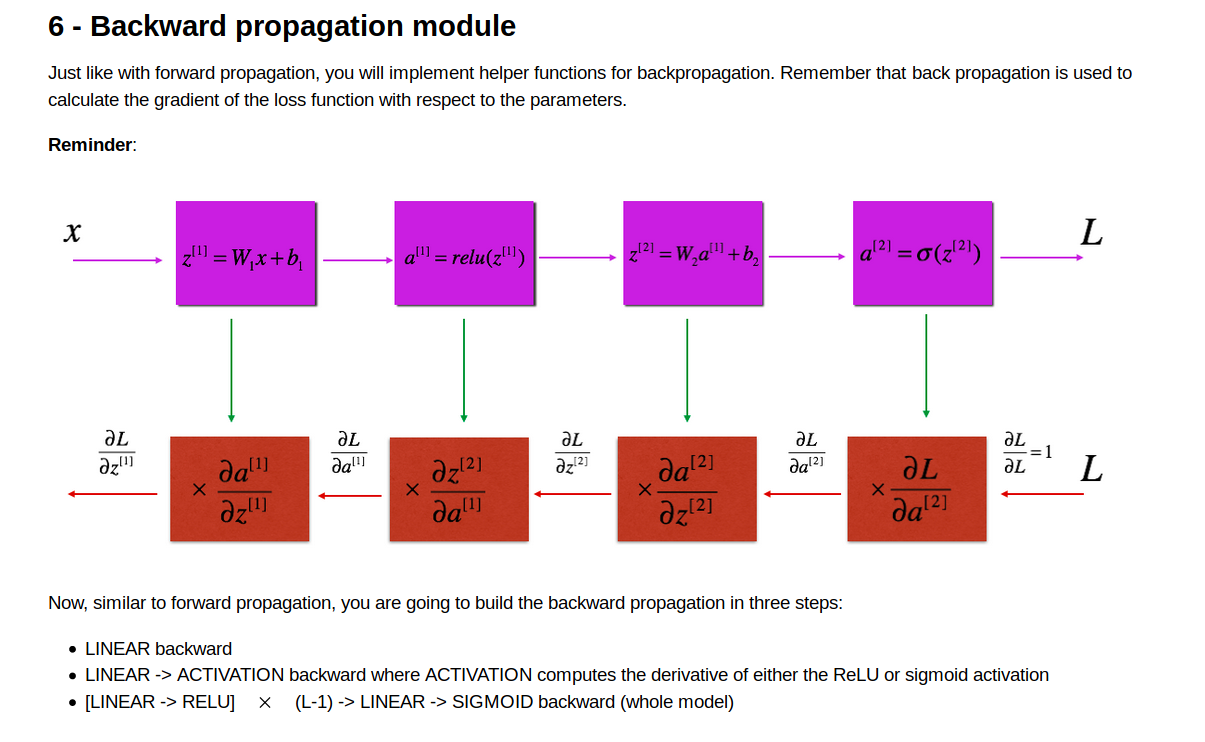
要通过计算dL/dz 来算出dw,dAprev,db 来进行梯度下降
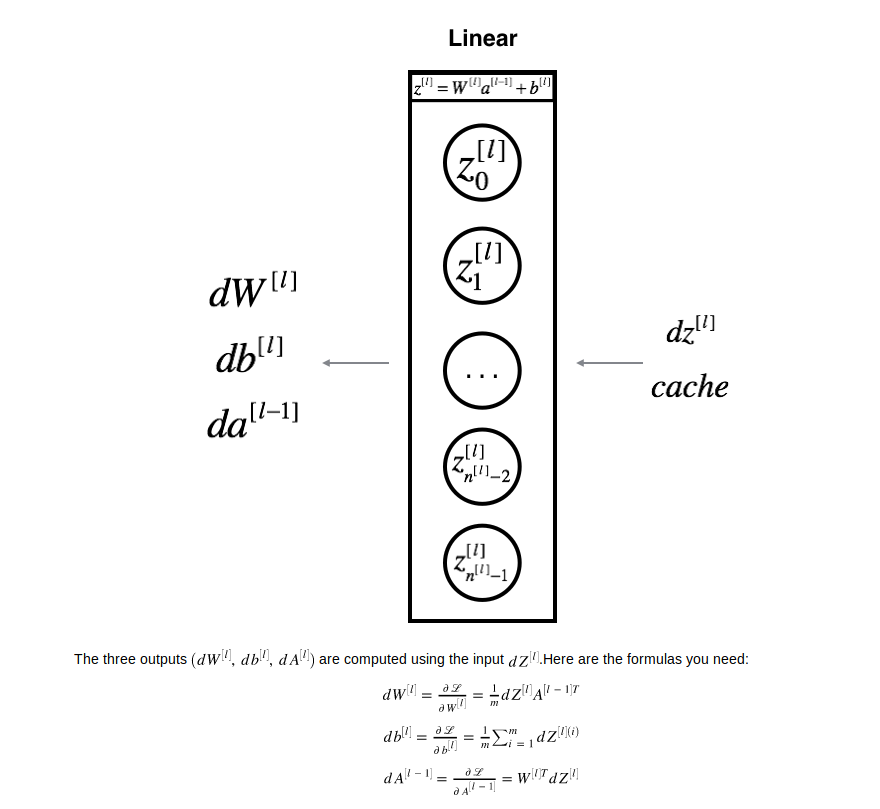
假设已知第l层的dZ,同时我们在做forward propagation的时候把对应该层的A_PREV,W已经存起来了
两个辅助函数
1 |
|
linear backward
计算公式如上图所示
1 | def linear_backward(dZ, cache): |
linear_activation_backward
那么上一个函数的dZ又是怎么计算?
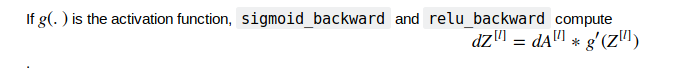
我们运用最开始定义的两个辅助函数来计算
1 | def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation): |
对L层的神经网络的backward
对最后一层是sigmoid_backward,剩下的所有层是linear_backward
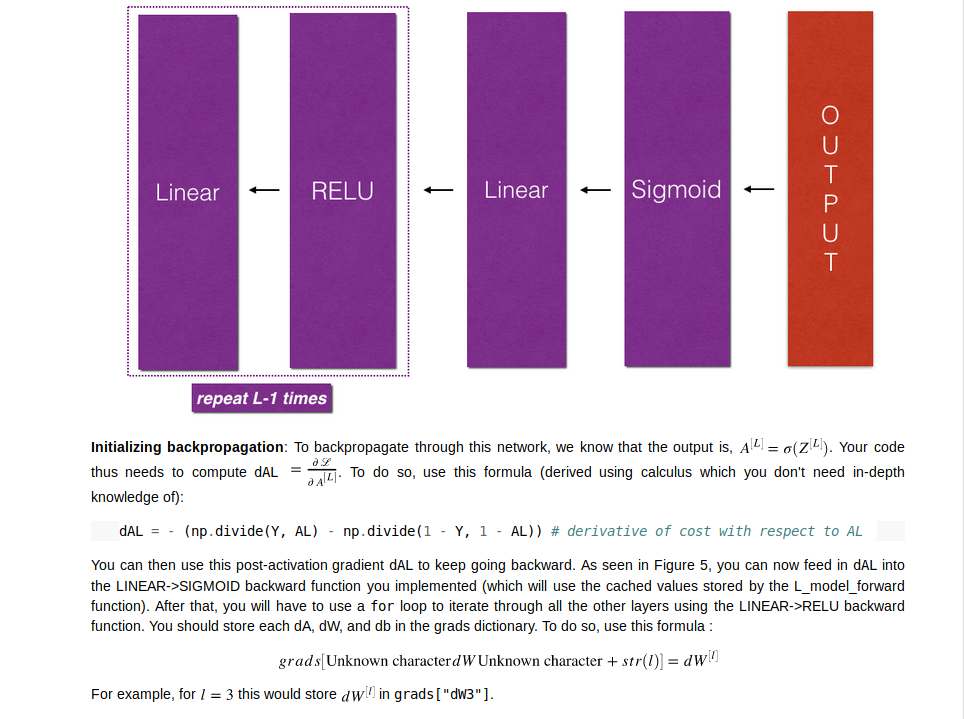
1 | # GRADED FUNCTION: L_model_backward |
更新参数
1 | def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate): |